Results
2,284 Results
Loading more Results ...
Loading more Results ...
Wine regions in Romania 11 growing regions
Description to Romania
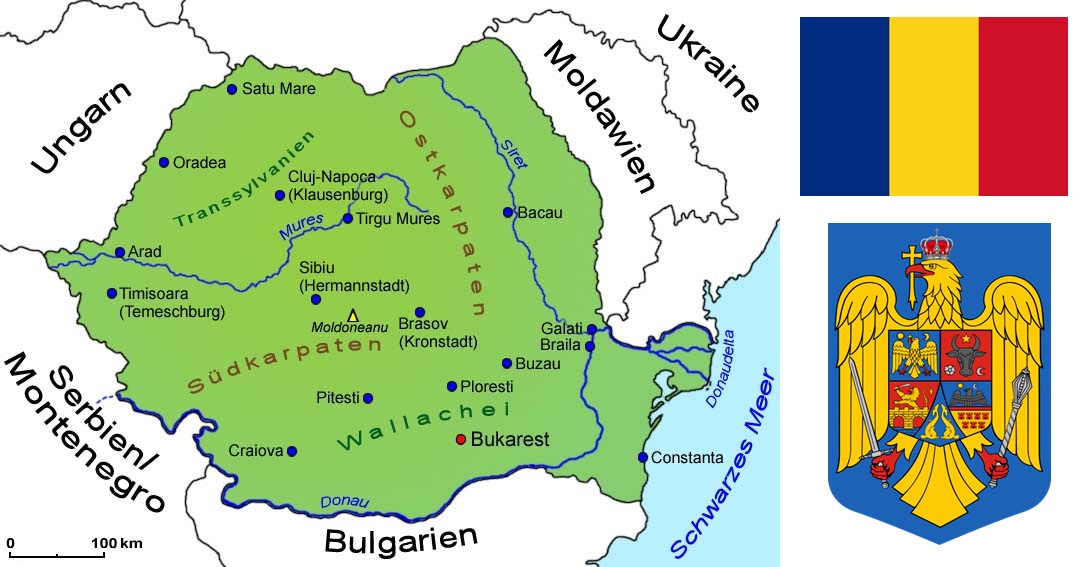
The Republic of Romania (România in Romanian, derived from the Latin Romanus) in south-east Europe with its capital Bucharest covers 238,397 km². The country lies on the Black Sea and stretches westwards across the Carpathian Arc to the Pannonian Plain. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Serbia and Hungary to the west and Ukraine and Moldova to the north and east. The state is divided into 41 counties (Județe) and the capital Bucharest.
History
With 6,000 years of wine history, Romania is one of the oldest and most traditional wine-growing countries in Europe. The Greek poet Homer already mentioned Thracian wines in his Iliad in the 8th century BC and the historian Herodotus (482-425 BC) tells of the wine trade of the Greek colonists on the Black Sea coast. German settlers from the Rhine-Moselle region followed the call of the Hungarian King Géza II (1130-1162), the ruler of this region at the time, and revitalised viticulture in Transylvania in the 12th century. In the 18th century, it was the Swabians who were brought into the country by the Habsburg ruler Maria Theresa (1717-1780). The historical landscape of Bessarabia, which today belongs to Moldavia, was mainly inhabited by Romanians at the beginning of the 19th century and belonged to Romania from 1917 to 1940.
Wine-growing regions
Romania belongs to the temperate climate zone and lies on the same latitude as France. Balanced rainfall, warm summers and long, dry autumns are ideal conditions for viticulture. However, the individual parts of the country differ climatically due to the natural barrier of the Carpathian Mountains. Transylvania west of the Carpathians is still characterised by the maritime climate of the Atlantic winds. However, the Carpathians prevent these from reaching the east and south of the country. Moldova (east of the Carpathians) is characterised by a continental climate with cold air currents from Ukraine. In Wallachia (south of the Carpathians) and Dobruja there are Mediterranean influences. The three most important regions are Moldova, Muntenia and Oltenia, where around 80% of Romanian wines are produced.
During the communist era, production was in the hands of the state. As a result of the political upheaval, a wave of privatisation set in from 1990 with many micro-owners. The leading production companies merged to form a private export distribution company. 487 wineries are registered as producers of authentic wines. A certification system for the origin and authenticity of wines enables traceability by means of a QR code (see centre image). There are 33 DOC/DOCC areas for quality wines or Prädikat wines(PDO = protected designation of origin) with 20,000 hectares and 12 IG areas for country wines(PGI = protected geographical indication) with around 6,500 hectares. The map shows the regions with their typical wine types. What Tokay is to Hungary, Cotnari is to Romania. This traditional wine was somewhat forgotten and has now been revitalised.
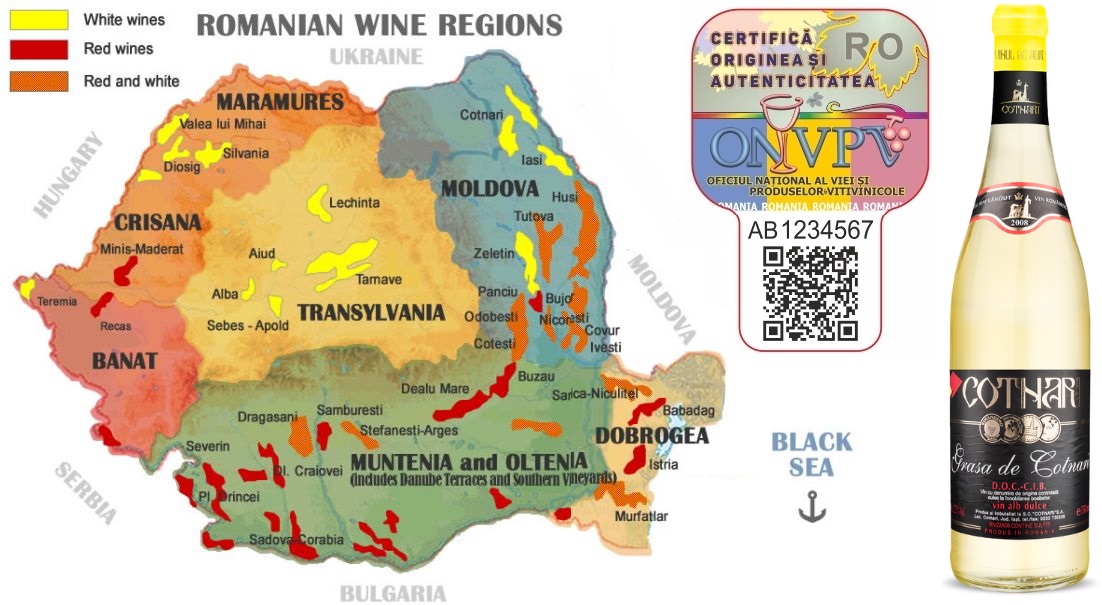
Banat
The region lies in the south-west of the country on the border with Serbia and Hungary. The wine-growing areas are Buzias-Silagiu, Dealul-Tirolului, Minis (known for its red wines from Cadarca and Cabernet Sauvignon), Moldova-Noua, Recas, Severinului and Teremia-Mare (known for its white wines from Riesling Italian = Welschriesling).
Crisana and Maramures
These two regions are located in the north-west on the borders with Hungary and Ukraine. The wine-growing areas are Diosig, Simleul-Silvaniei and Valea lui Mihai. Red and white wines.
Dobrogea (Dobrogea)
The region lies in the extreme south-east on the Black Sea and is bordered to the west by the Danube (Dunarea). The wine-growing areas are Istria-Babadag, Murfatlar, Ostrov and Sarica-Niculitel. In the sunniest climate in Romania with low rainfall, gentle red and rosé wines grow here.
Moldova (Moldavia)
The largest region with one third of the vineyard area is located east of the Carpathians in the east of the country on the border with Moldova and Ukraine. The wine-growing areas are Bujor, Cotesti, Cotnari, Covurlui, Dealul Bujorului, Husi, Iasi, Ivesti, Nicoresti, Odobesti, Panciu (known for its sparkling wines), Tutova and Zeletin.
Muntenia (Great Wallachia)
The region with the capital Bucharest is located in the south in the Southern Carpathians. The wine-growing areas are Dealurile Buzaului, Dealul Mare, Pietroasele, Samburesti and Stefanesti. The highest average temperatures in Romania can be found here. Today, the hilly region is best known for its red and rosé wines made from international varieties. In USSR times, these were preferably sweet.
Oltenia (Little Wallachia)
The region is located in the south-west of the country. The wine-growing areas are Corcova, Crusetu, Dealurile-Craiovei, Drăgășani, Drincea, Plaiurile-Drincei, Sadova-Corabia, Segarcea and Targu-Jiu. Excellent red wines are made here from the indigenous Fetească Neagră variety and Cabernet Sauvignon. The German winery Reh Kendermann acquired 350 hectares of vineyards here in 2001 and founded the "Carl Reh Winery".
Transilvania (Transylvania)
The region in the centre is particularly known for its white wines. German immigrants brought many of their own grape varieties with them. The wine-growing areas are Alba Iulia, Bistrita-Nasaud, Lechinta, Sebes-Apold and Tarnave.
Grape variety index
In 2022, the vineyards covered 187,934 hectares of vines and the wine production volume was 3.79 million hectolitres. Around 75% are white wines and 25% are red wines. A total of 163 grape varieties with almost 40,000 hectares are classified as "Noble Winegrape Varietes". Romania also has a significant production of table grapes; the most important are Afus Ali, Chasselas, Muscat d'Hamburg, Italia and Victoria. The grape variety index (ONVPV Romania):
Grape variety |
Colour |
Synonyms or Romanian name |
Hectare |
| Fetească Regală | white | Danasana | 12.213 |
| Fetească Albă | white | Dievcie Hrozno | 12.032 |
| Merlot | red | - | 11.109 |
| Welschriesling | white | Riesling Italian, Graševina | 6.964 |
| Sauvignon Blanc | white | - | 5.677 |
| Cabernet Sauvignon | red | - | 5.384 |
| Aligoté | white | - | 5.141 |
| Muscat Ottonel | white | Tămâioasă Ottonel | 5.124 |
| Fetească Neagră | red | Coada Răndunicii | 3.176 |
| Pamid | red | Roșioară | 2.652 |
| Băbească Neagră | red | Rara Neagră | 2.536 |
| Pinot Noir | red | - | 2.030 |
| Chardonnay | white | - | 2.002 |
| Muscat Blanc / Muscat | white | Tămâioasă Româneascâ, Tămâioasă Alba | 1.742 |
| Pinot Gris | white | - | 1.467 |
| Blaufränkisch | red | Burgundy Mare | 691 |
| Busuioacă de Bohotin | white | Busuioacă Neagra, Tămâioasă de Bohotin | 688 |
| Syrah | red | - | 638 |
| Gewürztraminer / Traminer | white | Traminer Roz, Rusa | 603 |
| Grasă de Cotnari | white | Grasă, Grasă Mare | 546 |
| Riesling | white | Riesling de Rhin | 453 |
| Galbenă de Odobești | white | - | 372 |
| Crâmpoșie | white | - | 366 |
| Rkatsiteli | white | - | 348 |
| Șarbă | white | - | 307 |
| Iordan | white | Zemoasa | 299 |
| Băbească Gris | white | - | 296 |
| Mustoasă de Măderat | white | - | 288 |
| Frâncușă | white | Frâncușe, Frîncușă | 277 |
| Blue Portugieser | red | Oporto | 229 |
| Cabernet Franc | red | - | 146 |
| Plavay | white | Plâvaie | 141 |
| Crâmpoșie Selecționată | white | - | 134 |
| Kadarka | red | Cadarcâ, Cadarcâ Neagră | 79 |
| Neuburger | white | - | 78 |
| Zweigelt | red | - | 76 |
| Novac | red | - | 73 |
| Sangiovese | red | - | 73 |
| Aromat de Iași | white | - | 62 |
| Negru de Drăgășani | red | - | 58 |
| Zghihară de Husi | white | Sghigardă Galbenă, Zghihară Galbenă | 57 |
| Alicante Henri Bouschet | red | Alicante Bouschet | 37 |
| Tempranillo | red | - | 31 |
| Select | white | - | 28 |
| Viognier | white | - | 28 |
| Ezerfürtű | white | - | 27 |
| Furmint | white | - | 26 |
| Alb Aromat | white | - | 25 |
| Codană | red | - | 25 |
| Bătută Neagră | red | Frâncușă Niagră | ? |
| Bagrina | white | Braghinâ, Braghină de Drăgășani | ? |
| Chasselas | white | - | ? |
| Coarnă Neagră | red | - | ? |
| Hárslevelű | white | - | ? |
| Creaca | white | - | ? |
| Slankamenka | white | Majarca Alba | ? |
Wine law & wine categories
In August 2009, the EU wine market regulation came into force with fundamental changes to wine designations and quality levels. There are the following new designations and quality levels (see Quality System):
- Vin (formerly Vin de Masă or table wine) = wine
- IG = Vin de Regiune or country wine
- DOC = Vin de Calitate or quality wine
- DOCC = corresponding to Prädikat wine
IG =Indicație Geografică or Vin de Regiune
The actual alcohol content must be at least 9.5% (for wine-growing zone B) or 10.0% vol (wine-growing zones CI and CII). The total alcohol content must not exceed 15% vol. There are around 50 rural wine regions, whose names are usually identical to the political district or region.
DOC = Denumire de Origine Controlată
Quality wines from specific growing regions with controlled origin. Prescribed quality wine grape varieties. The potential alcohol content must be at least 11.5%, the actual alcohol content at least 10% vol.
DOCC = Denumire de Origine Controlată si trepte de Calitate
This corresponds to a Prädikat wine. Minimum must weights are prescribed for each type. The codes refer to the degree of ripeness or proportion of noble rotten grapes; the second "C" refers to "Cules"(grape harvest):
- CMD (Cules la Maturitate Deplină) = Kabinett (73 Oe or 196 g/l sugar)
- CT (Cules Târziu) = late harvest (82 Oe or 220 g/l sugar)
- CS (Cules Selectionat) = Auslese
- CIB (Cules la Înnobilarea Boabelor) = Beerenauslese (125 Oe or 240 g/l sugar)
- CSB (Cules la Stafidirea Boabelor) = dry berry selection (noble rotten berries, Stafidirea = sultanas)
Special wine designations/types
- Vin Spumante cu Denumire de Origine Controlată = Sparkling wine with a designation of origin.
- Rezervă = Reserve (ageing for 6 months in oak barrels and 6 in bottle)
- Vin de Vinotecă (aged for 1 year in oak barrels and 4 months in bottle)
- Vin Tănăr = young wine (marketed until the end of the vintage year)
Map: © Goruma
Flag: by AdiJapan - Own work, Public domain, Link
Coat of arms: Public domain, Link
Cotnari: by Ulrich prokop - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
Wine-growing regions: Agroinform
Source 1st paragraph: WIKIPEDIA Romania
Classified wine producers in Romania 5
Recent wines 150
 Domeniile Averești
— Moldova (Moldau)
2022 Huși DOC Feteasca Neagra Dry "Diamond Selection"
Domeniile Averești
— Moldova (Moldau)
2022 Huși DOC Feteasca Neagra Dry "Diamond Selection"



